In biology immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Measurement of T cell subsets revealed a profound reduction in numbers of Th1 IFNγ CD4 and Tbet CD4 and Th17 IL-17 CD4 and RoRγt CD4 cells in decitabine-treated mice Fig.

T Cells And Cellular Immunity Medical Laboratory Medical School Studying Medical Laboratory Science
T Cell Development and Differentiation.

. Finally although estrogen has been reported to decrease activationinduced T cell proliferation E2BSA acting exclusively on membrane estrogen receptors enhanced cell growth. In general Th1 cells produce cytokines that promote cell-mediated immunity and include interferon IFN-gamma tumor necrosis factor TNF and IL-2. Humoral antibody-mediated immunity and cellular cell-mediated immunity.
Bennett MD in Mandell Douglas and Bennetts Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases 2020 Impact of Treatment on Cellular Immunity. Cytokines are small secreted proteins which mediate and regulate immunity inflammation and hematopoiesis. It is to note that prior investigations have attributed this estrogen-elicited action to an effect of the classical estrogen receptors 40 41.
The adaptive immune response is a specific defense mechanism of the immune system. Cytotoxic T cells T C are the key component of the cell-mediated part of the adaptive immune system and attack and destroy infected cells. The memory cell recognizes the antigen on subsequent infections causing the production of plasma cells that will produce the specific antibody.
They must be produced de novo in response to an immune stimulus. For this project I will be focusing on the humoral immune response. Cellular immunity is attributed to the action of.
They primarily attach bacterial invaders Cellular immunity is mediated by T Lymphocytes and combat intracellular infections such as viruses monitor cellular disruptions like tumors or foreign. As SARS-CoV-2 initially infects the upper respiratory tract its first interactions with the immune system must occur predominantly at the respiratory mucosal surfaces during both inductive. They generally although not always act over short distances and short time spans and at very low concentration.
Many of the bacteria that cause infectious disease in humans multiply in the extracellular spaces of the body and most intracellular pathogens spread by moving from cell to cell through the extracellular fluids. In the innate immune system natural killer NK cells play an important role for inhibiting cancer and metastases. The extracellular spaces are protected by the humoral immune response in which antibodies.
To establish its mechanism of action type II collagen-immunized mice were treated with decitabine or vehicle for 4 d as in the previous experiment. There are two main branches of the adaptive immune system. Th2 cells produce IL-4 IL-5 IL-6 and IL-13.
Therefore if the cell needs sodium ions all it has to do is open a passive sodium channel as the concentration gradient of the sodium ions will drive them to diffuse into the cell. Cellular immunity on the other hand targets and eliminates intracellular pathogens through the actions of T lymphocytes or T cells Figure 1813. For the past approximately five decades protective immunity was considered to be mediated by T cells but the resulting extensive testing.
The Humoral Immune Response - Immunobiology - NCBI Bookshelf. Activating antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells that are able to induce apoptosis in body cells displaying epitopes of foreign antigen on their surface such as virus-infected cells cells with intracellular bacteria and cancer cells displaying tumor antigens. In this way the action of an active transport pump the sodium-potassium pump powers the passive transport of sodium ions by creating a concentration gradient.
The mucosal immune system is the largest component of the entire immune system having evolved to provide protection at the main sites of infectious threat. Exposure to T cell lymphokines turns the macrophages into very aggressive phagocytes. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components.
Immunity is achieved by an individual through one of three routes. The process of eliminating T cells that might attack the cells of ones own body is referred to as T cell toleranceWhile thymocytes are in the cortex of the thymus they are referred to as double negatives meaning that they do not bear the CD4 or CD8 molecules that you can use to follow their pathways of differentiation Figure 2134. This is because viruses replicate within cells where they are shielded from extracellular contact with circulating antibodies.
Aging affects the innate immune system. Longer life in centenarians has been associated with increased NK cell number augmented interferon IFN-gamma production and phagocytosis 2123. Other components of the immune system adapt themselves to each new disease encountered.
Natural or innate immunity genetically inherited or acquired through maternal antibody acquired immunity conferred after contact with a disease and artificial immunity after a successful vaccination Also termed specific immunity resistance or specific resistance specific immunity is divided into cellular immunity. Cellular Molecular Immunology - Antitumor immunity induced by the photodynamic action of BAM-SiPc a silicon IV phthalocyanine photosensitizer. Regarding antibody-mediated autoimmune neurological disorders parkinsonism is in most cases a manifestation within the spectrum of each disorder and is attributed to the action of humoral and cellular immunity in brain regions such as the basal ganglia.
Both antigen-specific and antigen-nonspecific cells contribute to the development of cellular immunityThe antigen-specific branch of cell-mediated immunity can be divided into two major categories. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens irrespective of their antigenic make-up. It recognizes and targets specific antigens.
The age-associated increases in NK cells 21. The results were not good as heroin once again suppressed immunity. The results were not good as heroin once.
They act by binding to specific membrane receptors which then signal the cell. T-cell mediated immunity or T-cell immunity. T cells also play a more central role in orchestrating the overall adaptive immune response humoral as well as cellular along with the cellular defenses of innate immunity.
Innate and adaptive immune responses are intimately linked and controlled by sets of molecules and receptors that act to generate the most effective form of immunity for protection against fungal pathogens. T C cells are particularly important in protecting against viral infections. Cell Mediated Immunity Cell mediated immunity involves the actions of T cells and macrophages.
In the 1990s another branch of the network cellular immunity was explored. Cellular immunity protects the body through. The decision of how to respond will still be primarily determined by interactions between pathogens and cells of the innate immune system but the actions of T cells will feed.

The Immune System In Action Slh Interactive The Immune System In Action Add To Collection Add To New Collection Cance Immunity Immune Response Immune System

As I Mentioned Before Cellular Immunity Is The Adaptive Immunity In Which T Lymphocytes Directly Attack And Destroy Diseased Or F Immune Response Medical Cell
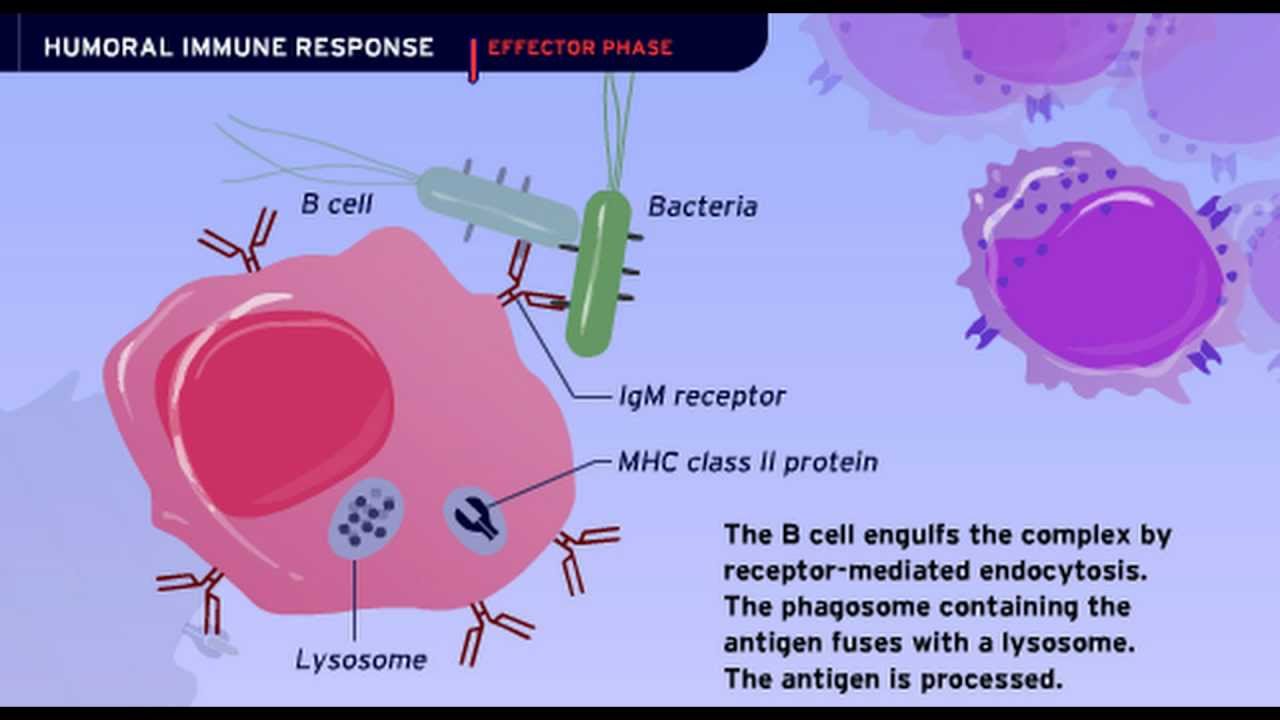
The Humoral Immune Response Medical Laboratory Science Human Anatomy And Physiology Immune Response
0 Comments